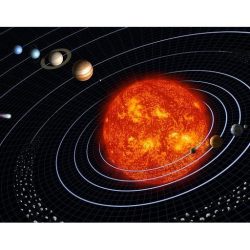
The solar system is a vast and intricate collection of celestial bodies, centered around the Sun, which is a medium-sized star. It comprises eight planets, including Earth, each with unique characteristics and orbits. In addition to the planets, the solar system contains dwarf planets, moons, asteroids, and comets, all of which contribute to its dynamic nature. The gravitational pull of the Sun governs the movements of these bodies, creating a delicate balance that has persisted for billions of years. This complex system not only showcases the diversity of planetary environments but also serves as a focal point for astronomical research and exploration.
The sun, a colossal ball of hydrogen and helium, serves as the central star of our solar system, providing the essential light and heat that sustain life on Earth. Its immense gravitational pull keeps the planets in orbit, while its nuclear fusion processes generate energy that radiates outward, influencing climate and weather patterns. The sun’s surface temperature reaches approximately 5,500 degrees Celsius, and its core, where fusion occurs, can exceed 15 million degrees Celsius. This powerful star not only illuminates our days but also plays a crucial role in the intricate balance of ecosystems, making it a vital component of our existence.